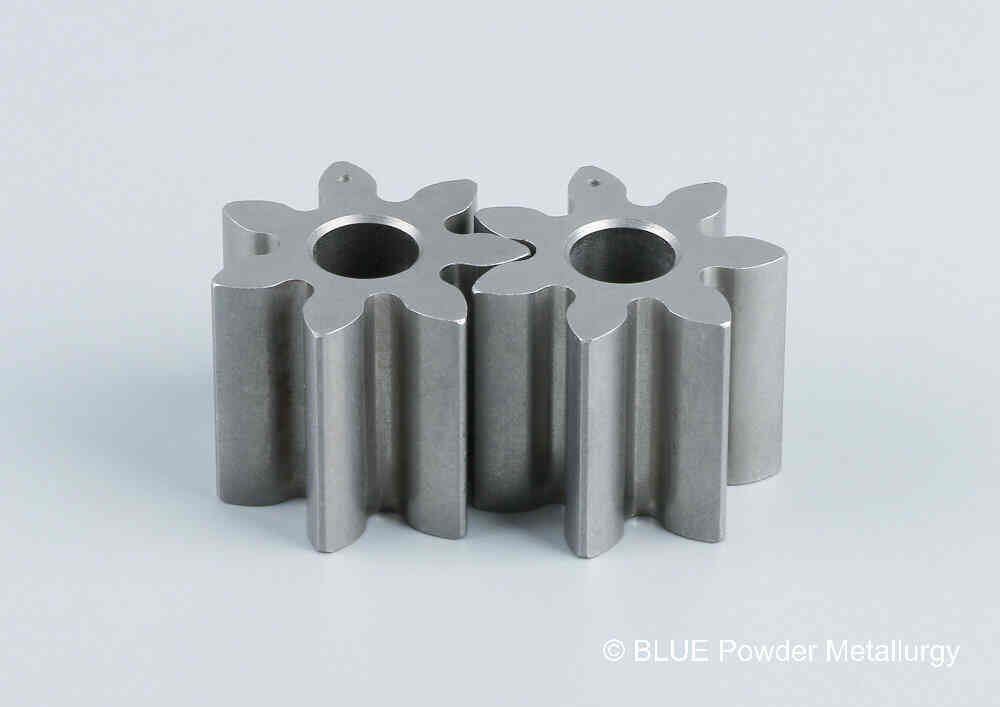
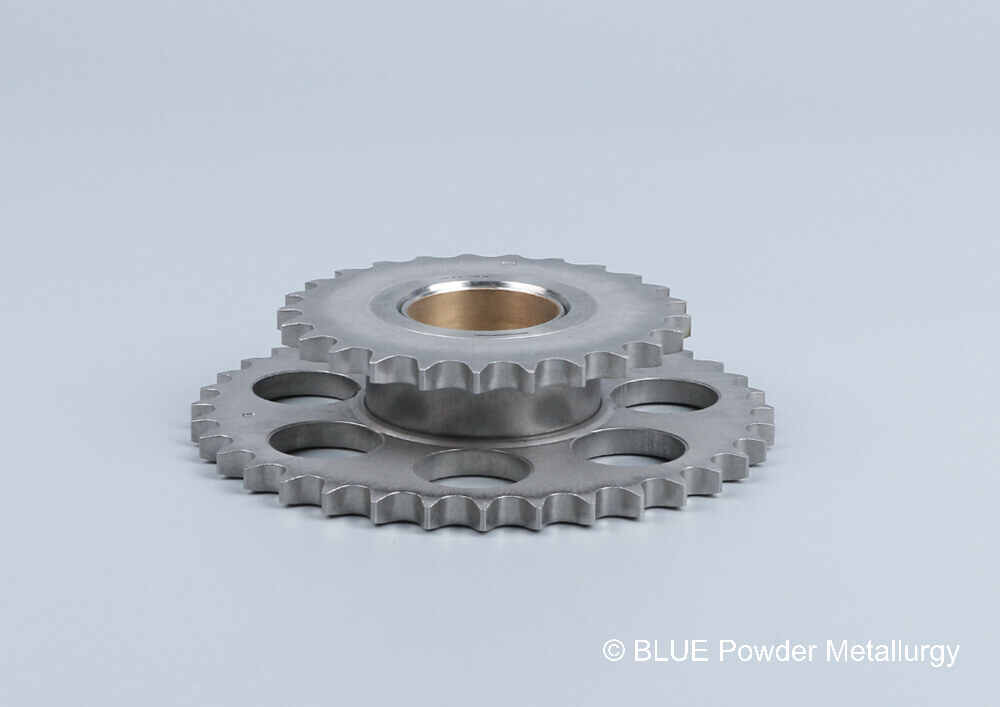
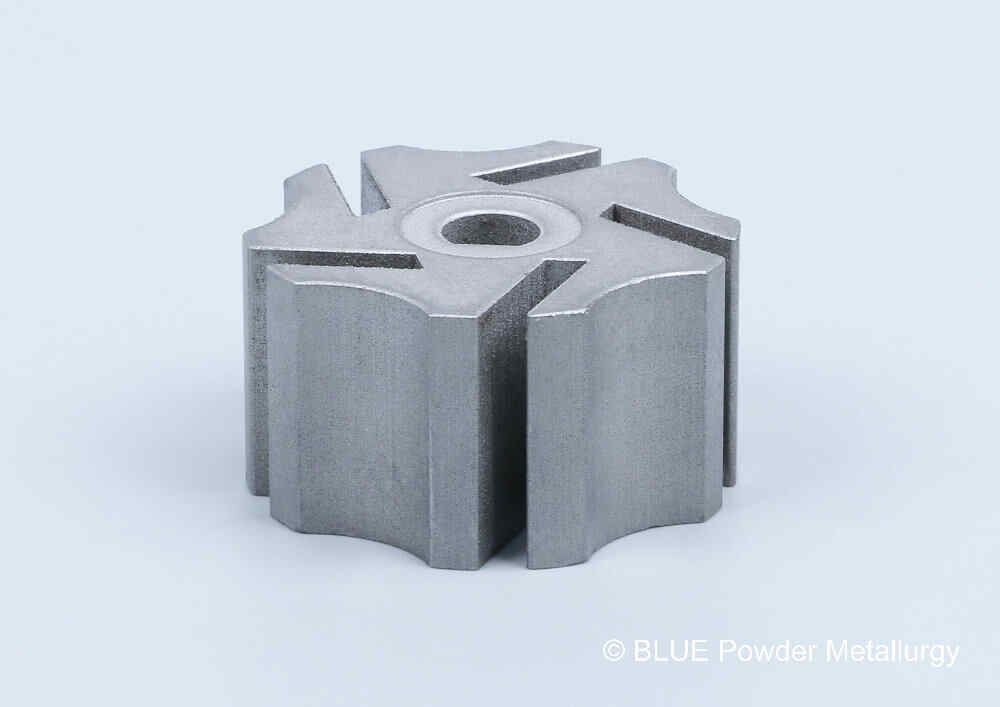
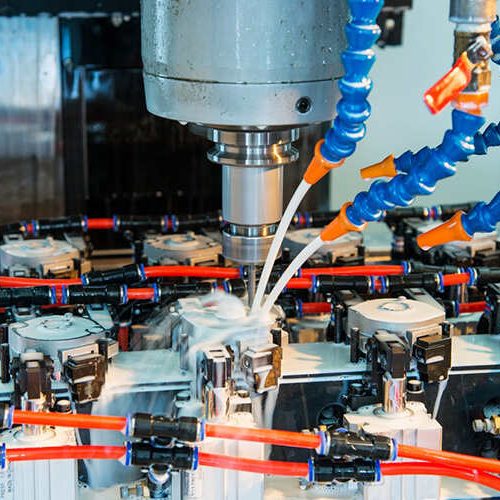
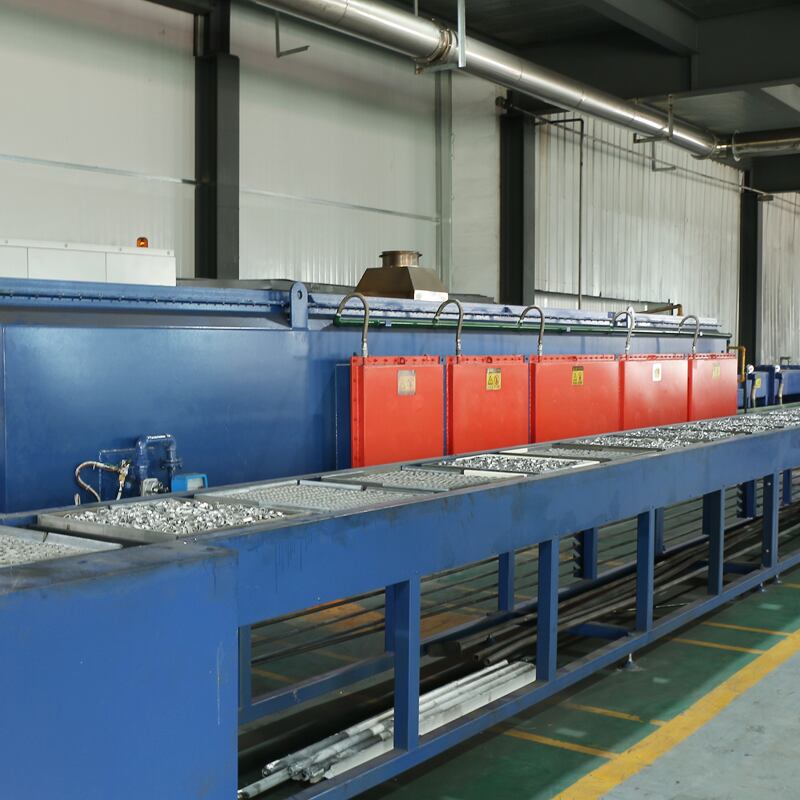
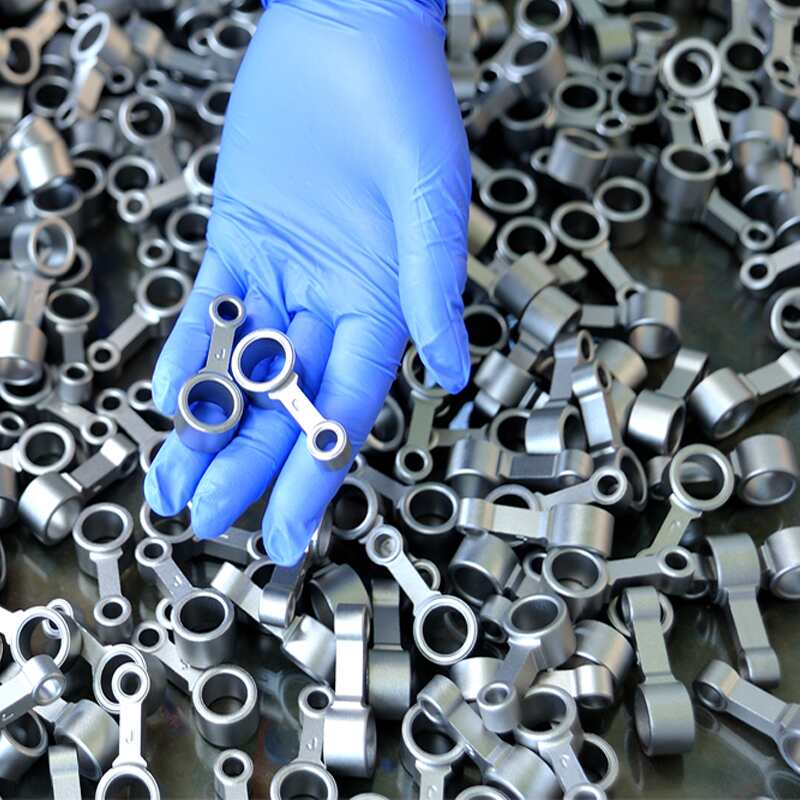
Prealloyed low-alloy steel powders in powder metallurgy are made with nickel, molybdenum, manganese, and chromium as key alloying elements, with graphite added to achieve the desired carbon content.
These materials are favored for medium- to high-density applications where heat-treated parts must deliver high strength and wear resistance, offering greater hardenability than copper- or nickel-steel blends.
Common material designations include:
| Material Grade | Fe | C | Ni | Mo | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL-4005 | Bal. | 0.4–0.7% | — | 0.40–0.60% | 0.05–0.30% |
| FL-4205 | Bal. | 0.4–0.7% | 0.35–0.55% | 0.50–0.85% | 0.20–0.40% |
| FL-4405 | Bal. | 0.4–0.7% | — | 0.75–0.95% | 0.05–0.30% |
| FL-4605 | Bal. | 0.4–0.7% | 1.70–2.00% | 0.45–0.60% | 0.05–0.30% |
| FL-5305 | Bal. | 0.4–0.6% | — | 0.40–0.60% | 2.7–3.3% |