Graphite is a non-metallic material, but it has metal-like properties, such as thermal and electrical conductivity, and has a wide range of applications.
Therefore, graphite is widely used in refractories, batteries, casting, and friction materials.
The table below shows the application share of natural graphite and artificial graphite in different industries in 2024.
| Applications | Natural Graphite | Synthetic Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | 52% | 31% |
| Electrodes | / | 47% |
| Refractories | 24% | 1% |
| Castings | 8% | 1% |
| Friction Materials | 3% | 2% |
| Lubricants | 3% | 3% |
| Recarburising | 2% | 8% |
| Graphite Shapes | 1% | 4% |
Contents
What is Graphite?
Graphite is a soft, black, crystalline carbon in metamorphic rocks like marble, schist, and gneiss.
It is very stable, has high electrical and thermal conductivity, and is resistant to high temperatures.
Graphite includes natural graphite and synthetic graphite. Natural graphite exists in three forms, flake, crystalline, and amorphous, and synthetic graphite includes isostatic graphite, extruded graphite, molded graphite, etc.
Structure and Properties of Graphite
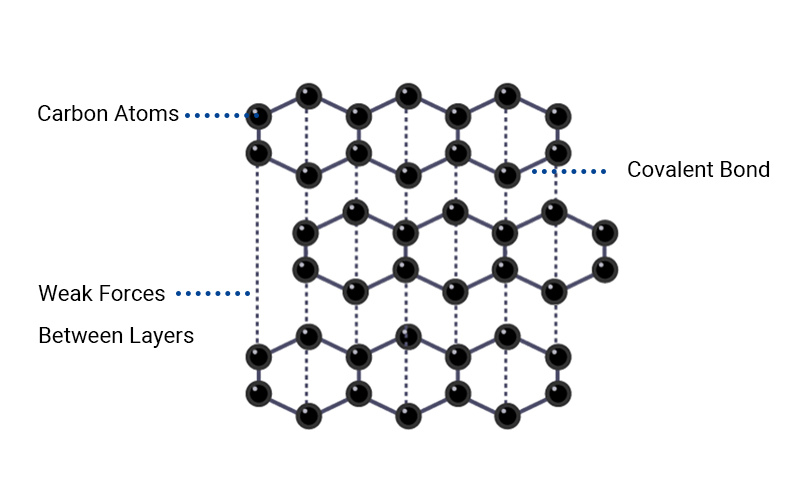
Graphite has a 2D layered hexagonal crystal structure. Each layer of carbon atoms is arranged in a honeycomb shape, and there are weak van der Waals forces between the layers.
Use of Graphite
You can see graphite is utilized in a variety of industries, from traditional manufacturing processes to new energy materials, to lubrication and flame retardant materials.
Graphite Electrodes
The largest application market for synthetic graphite is graphite electrodes because of its good electrical conductivity. Like metal materials, graphite has delocalize free electrons those are free to move and conduct electricity. Graphite electrodes are primarily used in electric arc furnaces and also play a key role in ladle furnaces and other smelting processes for refining steel.
Refractory Materials
Graphite has the advantages of oxidation resistance, good thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and low expansion coefficient. It is an important material in the refractory industry.
Flake graphite is often used as a cover layer for metal melts because it can withstand high temperatures of more than 3000℃ and can dissipate heat.
Li Battery
Graphite is an ideal anode material for lithium-ion batteries with the following advantages:
- Long cycle life and stability
The layered crystal structure of graphite can remain stable during repeated lithium ion insertion and extraction, which makes lithium batteries have excellent cycle performance and durability.
- High capacity
Graphite can effectively store lithium ions, providing high energy density and improving the energy storage capacity of batteries.
- Cost-effective
Compared to other metal anodes, natural and synthetic graphite is cost-effective.
Powder Metallurgy
In the powder metallurgy industry, graphite has two main functions:
- Lubrication
Graphite is a good dry lubricant, which is beneficial to improve the friction performance of powder metal parts. Typical applications are: self-lubricating sintered bushings, valve guides, valve seats. It is also used for sintering brake pads, clutch friction plates, linings.
- Alloying elements
During the mixing stage, graphite powder is added to the metal powder as an alloying element.
During the sintering process, graphite powder diffuses into the sintered part matrix, effectively improving its hardness, tensile strength and fatigue durability.

LED Industry
Graphite is used in LED Light heat sinks to dissipate heat efficiently, ensuring longer LED lifespan and stable performance.
Compared to traditional aluminum heat sinks, graphite-based heat spreaders offer better thermal conductivity while being lightweight.
Automotive
You will also see graphite materials used in the automotive industry. For example, in automotive brake linings, carbon seals, bearings, washers and clutches, graphite can provide good friction and heat dissipation properties.
Aerospace
Graphite is favored by aerospace engineers because of its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and good thermal conductivity.
Weight reduction is very important for aerospace because it can reduce fuel consumption and reduce costs.
Graphite’s self-lubricating properties and high temperature resistance over 3000℃ make it a great choice for aerospace seals, bearings, and valves.
Casting
Graphite is also commonly used in continuous casting molds. It has the following advantages:
- Low thermal expansion coefficient & high temperature resistance
During casting, the mold is subjected to very uneven temperatures. The low thermal expansion coefficient of graphite prevents it from deforming or cracking.
- Good lubricity
Graphite’s good self-lubricating properties reduce the friction between the mold and the casting material, which is beneficial for demolding of castings.
- Durability and cost
Graphite molds have good durability, long service life, and relatively low cost.
- Good chemical inertness
Graphite can resist chemical reactions with molten metal and maintain the integrity of the mold.

Painting & Writing
Graphite is soft and black in color and can be used to make both traditional wooden pencils and mechanical pencils with replaceable leads. The “hardness” of a pencil depends on the ratio of graphite to clay.
You can draw and write with graphite pencils, and they can be easily erased from paper.
FAQ
What is the Theoretical Density of Graphite?
The theoretical density of graphite is 2.26g/cm3, but the density of synthetic graphite is generally 1.6-1.9g/cm3.



