Due to high demand of Nickel plating in various industries such as decorative, aerospace, electronics, and telecommunications, 150,000 tons of electroplated nickel is deposited every year. The market size of nickel electroplating in 2024 was about USD 2.80 billion, and it is expected to increase to USD 3.83 billion by 2033.
Contents
What is Nickel Plating?
Nickel Plating is a technique in which a layer of nickel or its alloy is deposited over other materials such as steel, ABS, brass, copper, or nylon. This technique aims to enhance the mechanical and physical properties of the surface of various components. two main methods: nickel electroplating and electroless nickel plating.

History of Nickel Plating
Luigi Brugnatelli invented the process of electroplating in the 19th century. Initially, it was used to plate gold or silver to create decorative items and jewellery. Later on, Golding Bird developed a nickel sulfate solution for electroplating medical instruments. Over time, various nickel alloys were created for electroplating, and today, nickel electroplating is performed using different nickel-based solutions tailored to meet the needs of specific components and industries.
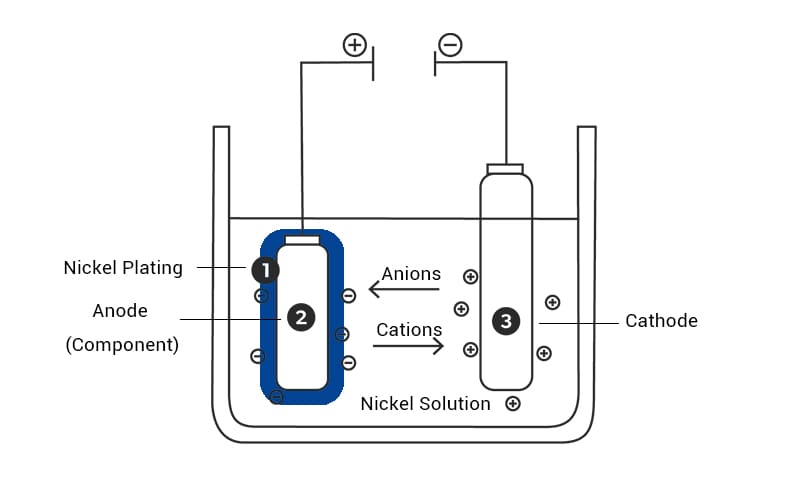
What is the Nickel Plating Process?
Here is step by step electroplating process
- Surface cleaning and degreasing: In this step, any oil and oxides are removed from the surface of the metal using cleaning agents often assisted by ultrasonic agitation.
- Acid activation and pickling: The surface is treated with acids like hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid in order to remove the dissolved oxides and activate the substrate surface. Here the pH is controlled within 3.5–4.5.
- Electrolytic nickel deposition: In an electrolytic cell, the substrate (cathode) and pure nickel anodes are immersed in a nickel solution whose temperature is maintained between 40–70 °C, usually nickel sulfate or sulfamate bath. Ow a DC is applied, causing Ni²⁺ ions to migrate and reduce onto the cathode surface via the reaction: Ni²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ni (s).
This results in the formation of a dense, adherent nickel coating.
- Posttreatment: Here, the coated surface is rinsed with deionized water to remove any leftover electrolytes. Passivation of the layer is done by treating it with nitric acid, which helps develop a stable oxide layer, and finally, hot air is used for drying.
Quality Control Measures
- Coating Thickness Measurement: To check out whether the coating thickness is within specific range or not some techniques are used such as XRF, magnetic induction, and eddy current
- Adhesion Testing: To measure the adhesion strength of coating with surface of substrate tests like peel, scratch, and pull-off are done.
- Visual and Optical Inspection: Here, microscopes or 3D scanners detect defects like cracks, pitting, or uneven layers.
- Corrosion resistance testing: To check how well the electroplated layer resists degradation in harsh conditions, the salt spray test, humidity test, and cyclic corrosion tests are performed.
Benefits of Nickel Plating
Corrosion resistance
Nickel plating acts as a barrier against moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making the metal resistant to corrosion.
Conductivity
Since nickel is a good conductor when plated on the surface of components, it enhances their conductivity. The connectors and circuit boards, which are plated with nickel, show more effective electrical performance.
Visual Appeal
Nickel provides a shiny or matte finish with a bright, polished look. This property makes it ideal for decorative purposes.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Nickel coating boosts the surface hardness and wear resistance. This property makes the components long-lasting and ideal for working under harsh conditions.
Heat Resistance
Nickel plating provides increased resistance to heat, protecting components from high-temperature environments.
Lubricity
Nickel plating can also enhance the lubricity of a component’s surface, reducing friction and wear in moving parts.
Types of Nickel Plating
Electrolytic Nickel Plating
Bright Nickel Plating
It is mainly used for decorative finishes due to its high luster and leveling properties. In this type of nickel plating organic additives (carriers and levelers) control the growth of nickel crystals. These organic additives enhance brightness and leveling properties of coating.
Satin Nickel Plating
Satin nickel plating,also known as pearl nickel printing, is a technique in which electroplating is done by particle co-deposition. In this plating fine particles like silica are embedded into the nickel which disrupts crystal growth to scatter light. Satin nickel plating is widely used on doors, furniture and other hardware because it produces a beautiful satin or semi-gloss finish.
Black Nickel Plating
Black nickel plating typically results in a thin black layer deposition of about 0.2-1.0 µm thickness. It shows poor corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance properties. In this technique, a mixture of nickel and zinc, along with sulfur compounds, is utilized. It is utilized for decorative purposes and glare reduction in optical and electronic components.
Electroless Nickel Plating
What is electroless nickel plating? It is a chemical process that involves the deposition of a nickel-phosphorus alloy onto a substrate. In this process, no external circuit current is needed; it involves a self-catalytic reaction. It is divided into three types depending on the phosphorus composition:
High-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel Plating: This type of electroless nickel plating contains 10-12% phosphorus. Its coating provides highest corrosion resistance of all the EN deposits, especially in acidic environments, good ductility,and hardness of about 45-57HRC
Medium-Phosphorus: Electroless Nickel Plating: It contains 6-9% phosphorus. It is a widely used type of plating that balances corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Low-Phosphorus Electroless Nickel: This offers the highest hardness (58-62 HRC) and wear resistance among electroless nickel types. It contains 1-4% phosphorus.
What is a Nickel Plating Solution?
This solution is a chemical bath used in the electroplating process to deposit a thin layer of nickel onto a substrate. The type of solution and its parameters, such as pH, temperature, and current density determine the quality and properties of the nickel coating.
Types of Electrolytes Used
Watts Nickel Solution (Sulfate-based):
Most nickel plating solutions, especially for decorative plating, are based on the “Watts” formula developed by Professor Oliver P. Watts.
It is a mixture of nickel sulfate (NiSO₄), nickel chloride (NiCl₂), and boric acid (H₃BO₃).
| Component / Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nickel sulfate (NiSO₄·6H₂O) | 240 – 300 g/L |
| Nickel chloride (NiCl₂·6H₂O) | 30 – 90 g/L |
| Boric acid (H₃BO₃) | 30 – 45 g/L |
| Temperature | 40 – 60 °C |
| pH | 3.5 – 4.5 |
| Cathode current density | 2 – 7 A/dm² |
| Deposition rate | 25 – 85 µm/h |
Sulfamate Nickel Solution
It contains nickel sulfamate (Ni(NH₂SO₃)₂) solution and it is Ideal for producing thick, low-stress nickel coatings with smooth finishes.
| Component/Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Nickel sulfamate (Ni(NH₂SO₃)₂) | 300 – 450 g/L |
| Boric acid (H₃BO₃) | 30 – 40 g/L |
| Temperature | 40 – 60 °C |
| pH | 3.5 – 4.5 |
| Cathode current density | 2 – 15 A/dm² |
Chloride-based Solutions
These are modified Watts-type baths with higher nickel chloride (NiCl₂) concentrations. These baths provide better conductivity, macro-throwing power, and anode dissolution. They operate at temperatures between 40–70°C.
What Materials Can be Nickel Plated?
Steel: Nickel plating on steel improves corrosion resistance, hardness, and strength, thus making it ideal for its use in engineering applications.
Zinc and Zinc Alloys: Nickel enhances Zinc’s durability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for industrial goods and auto motives.
Copper: Plating the copper with nickel coating results in more effective conduction, leading to its use in manufacturing connectors, terminals, and wiring.
Aluminum: Although it needs pre-treatment before nickel plating, its plating results in increasing its surface strength and durability.
Brass: Nickel plating on brass provides enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and a polished appearance. It is often used in decorative items and electrical connectors.
What is Nickel Plating Used For?
Powder Metallurgy Parts
Wear and corrosion are common issues with powder metallurgy parts, as their interconnected porosity encourages corrosion within pores, limiting their potential applications. Nickel electroplating can effectively enhance corrosion resistance and improve surface finish.
Nickel electroplating needs the pores in PM parts to be filled, but chemical nickel plating does not.

Automotive Industry
Nickel plating is used to coat automotive parts like engine components, fuel systems, and trim parts because it offers corrosion and wear protection to the components.
Aerospace
It is applied to aerospace components such as turbine blades, gears, and landing gears. It provides excellent corrosion protection, wear and erosion resistance as well as adhesion and hardness.
Electronics
Due to high solderability and corrosion resistance, nickel plating is used on connectors, switches, and contacts.
Medical
Since Nickel plating offers wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility to the surface of components, it is used in medical devices. This ensures the longevity and reliability of devices in contact with the human body.
FAQ
1. What is Zinc Nickel Plating?
It is a corrosion-resistant electroplating process where a nickel-zinc alloy is deposited onto a substrate. It offers improved corrosion protection compared to traditional zinc plating.
2. What is Nickel Chrome Plating?
A two-layer electroplating process where a layer of nickel is applied first, followed by a thin layer of chromium. It not only provides high corrosion resistance and durability but also a reflective, shiny finish.
3. What Color is Nickel Plating?
It is typically a silvery-white color. Its color can vary with variations in brightness depending on the type and additives used.







