For some parts with large aspect ratio, complex shapes, uniform density and strength requirements, conventional uniaxial pressing is almost impossible.
Cold isostatic pressing (CIP) is a feasible technology.
What is Cold Isostatic Pressing?
Cold Isostatic Pressing is a powder forming technique where uniform pressure (5,000 psi to 100,000 psi, equal to 34.5 to 690 MPa) is applied from all directions to a powder, in a flexible mold, at room temperature, to create the green part.
Contents
Cold Isostatic Pressing Process
The manufacturing process of cold isostatic pressing is as follows:
First, a male mold with the same shape as the product is made, and a female mold is cast on the outside with rubber.
Then, powder metal is filled into the mold and sealed with a cover. In order to reduce mold deformation, the mold needs aluminum and steel shells to support deformation.
Finally, the manufacturer immerses the mold in oil or other liquid, applies pressure after sealing the hatch, and compacts the powder into a near-net-shape product through hydraulic pressure.
Types of Cold Isostatic Pressing
There are two types of CIP: wet bag and dry bag.
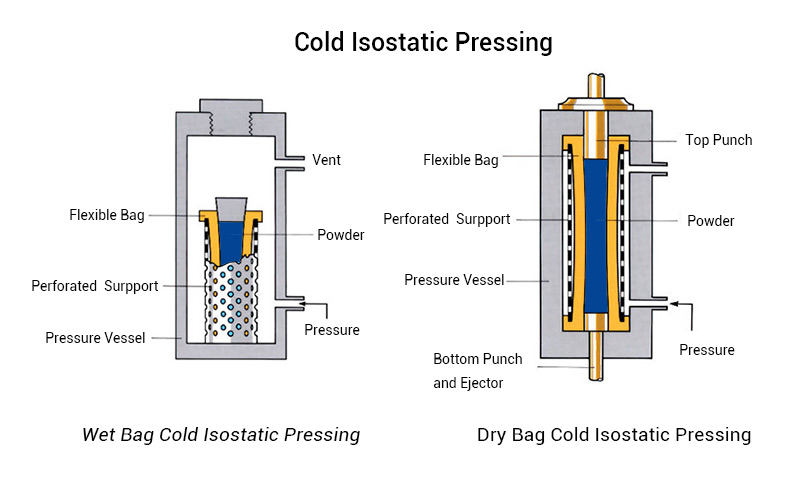
Wet Bag Isostatic Pressing
The wet bag method is to completely immerse the mold in oil or other liquids for pressing.
The mold is subjected to pressure from all sides, so the density of the green body is relatively uniform.
However, the production rate is slow and it is not easy to automate production. Therefore, wet bag cold isostatic pressing is used for small batch production and prototyping of special parts.
Dry Bag Isostatic Pressing
In the dry bag process, the bottom of the mold is fixed to the equipment, and only the mold or the mold and its top are surrounded by liquid. So it is not true isostatic pressing. However, the dry bag method has high production efficiency because it is convenient to fill materials and remove workpieces, and it is easy to automate.
Advantages of Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Process Refractory Metals
Cold isostatic pressing can process high melting point metals such as tungsten, which cannot be easily cast.
- Longer Aspect Ratio
CIP can manufacture parts with relatively long lengths, which cannot be produced by uniaxial pressing.
- Low Mold Cost
The mold material for cold isostatic pressing is generally natural rubber or polyurethane rubber. Compared with traditional powder pressing using expensive tool steel, it is cheaper.
- Uniform Density & Strength
The workpieces produced by CIP have uniform density and strength because each part of the green part is subjected to uniform pressure. When these parts are sintered later, there will be uniform shrinkage.
- Good Green Strength
Metal parts produced by cold isostatic compaction have good green strength.
- Complex Geometric Shapes
CIP can make components with three-dimensional features.

Limitations of CIP
- The disadvantage of cold isostatic pressing is that it cannot produce high-precision parts. You must perform secondary processing after the green part is sintered to achieve tight tolerances.
- The maximum molding pressure of cold isostatic pressing is limited to about 600MPa.
Applications of Cold Isostatic Pressing
Cold isostatic pressing has broad applications in powder metallurgy, refractory metals, sputtering targets, and ceramic manufacturing.
Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is a recognized green manufacturing process that uses metal powder as raw material. The metal powders are pressed into a mold cavity to form the desired shape and sintered to obtain the expected physical and mechanical properties.
However, the conventional powder metallurgy process uses uniaxial pressing, which makes it difficult to produce products with large aspect ratios. Cold isostatic pressing can produce parts with large aspect ratios, such as porous metal tubes.

Refractory Metals
Some refractory metals such as tungsten, molybdenum and tantalum are difficult to process with traditional manufacturing processes. Cold isostatic pressing can process these refractory metals without melting them, with high material utilization and low energy consumption.
Sputtering Targets
Sputtering targets are the source material used in the sputtering process, a thin-film deposition technique.
CIP can make indium tin oxide (ITO) powder in larger shapes, and after sintering process, a product with a density of 95% can be obtained.
Ceramic
Ceramics have important applications in modern industry due to their excellent high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and insulation properties.
Ceramics have a variety of production routes, including compression molding and isostatic pressing. Through CIP, manufacturers are able to produce ceramic parts with complex shapes and uniform density.
BLUE is a dedicated powder metallurgy company, certified to ISO 9001:2015 and backed by 20 years of manufacturing experience. Our capabilities include conventional powder metallurgy processes, metal injection molding, isostatic pressing, and can process metals, plastics, and ceramic materials.
We provide standard powder metal parts and customized services. If you need cold isostatic pressing services or metal powder products, please contact us, we are willing to work for you!
FAQ
1. How Do Uniaxial Pressing and Isostatic Pressing Compare?
Uniaxial pressing and isostatic pressing are two common powder compaction methods used in powder metallurgy and ceramic manufacturing.
- Uniaxial pressing uses a rigid die, such as tool steel, to apply pressure to the material in a “single direction”(typically vertical) through a punch. Isostatic pressing uses a fluid in a sealed chamber to apply pressure evenly from “all directions”.
- The density of products produced by uniaxial pressing is not uniform, while products made by isostatic pressing have uniform density.
- Uniaxial pressing is suitable for large-scale production, whereas isostatic pressing is ideal for small-batch manufacturing.
2. What are the Differences between Cold and Hot Isostatic Pressing?
Cold isostatic pressing is performed at room temperature, while hot isostatic pressing is performed at high temperature.
The main purpose of CIP is powder compaction before sintering process. HIP removal of internal pores can produce a completely dense product.
The pressure medium of cold isostatic pressing is liquid (usually oil or water), while the pressure medium of hot isostatic pressing is inert gas (typically argon).
3. Do Parts Made by Cold Isostatic Pressing Require Sintering?
Yes. CIP is a powder pressing technology that requires sintering to fuse the powder particles together. After the sintering process, the parts can obtain the desired mechanical properties.