Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and Die Casting both use high pressure to fill materials into the mold cavity. Their mold systems consist of two parts and work in a similar principle.
What is the key difference between them?
Die casting utilizes the molten metal as raw material, while metal injection molding utilizes the metal powders and binders.

Contents
What is Metal Injection Molding?
Metal Injection Molding Process
The metal injection molding process is shown in the figure below.
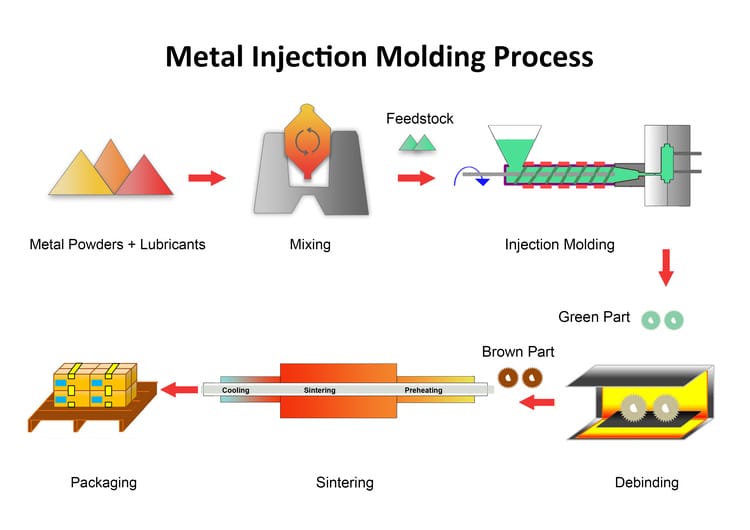
Mixing
In this process, you mix metal powder and binders to create the “feedstock.” Adding binders reduces the friction between metal powders and makes them fluid. The ratio of metal powder to binders is usually around 60:40.
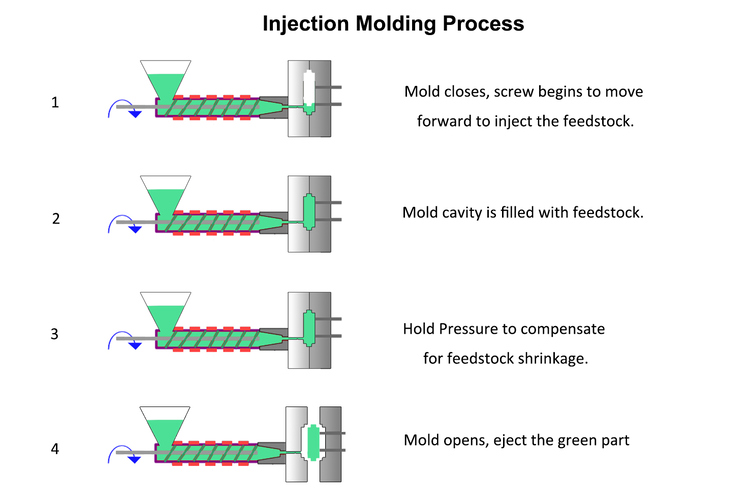
Injecting
After the mixing process, the metal injection molding machine injects the feedstock into the die cavity. After the green compact is cooled and shaped, the mold is opened and the injection pin ejects it. This is much like plastic injection molding.
Debinding
Debinding is to remove binders to prevent them from affecting the quality of the finished product. The green parts after debinding process are called brown parts.
You may know about thermal debinding, which is very cheap, but too slow. If you want faster, solvent debinding and catalytic debinding are necessary.
Sintering
The green density of injection molding is very low and cannot meet the requirements of finished products.
Sintering is to give brown parts mechanical and physical properties. In this process, you send unfinished products to the sintering furnace to heat below their melting points. This works like the conventional PM process.
It should be noted that the sintering shrinkage of metal injection molding parts is very large, about 15%.
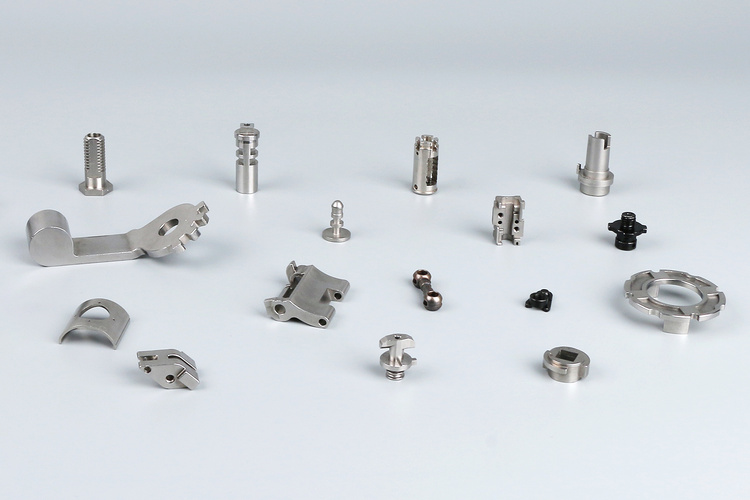
Metal Injection Molding Applications
Automotive
Metal injection molding is indispensable in the automotive industry due to its large batch production capacity, high density, and superior precision. Some automotive parts you may have seen, include fuel injection components, shift levers, electrical connectors, and airbag initiators.
Medical
Metal injection molding has also contributed to the development of the medical industry.
Orthodontic brackets are a typical MIM product. Others include surgical instruments, biocompatible implants, and medical devices.
Aerospace
Engineers favor lightweight and high-strength aerospace parts. This ensures flight safety and saves fuel. Metal injection molding has the ability to provide outstanding products, such as aerospace engines and seatbelt components. Meanwhile, they can also produce components with complex geometries.
Electronics
The surface roughness of MIM products is good, which is favored of consumer electronics products. For example, your smartphone frame, camera bracket, and card tray are also manufactured using MIM technology.

Metal Injection Molding Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Small Parts
- Complex Shapes
- Consistent Quality
- Material Utilization
- Product Density & Strength
- Design Flexibility
Disadvantages
- Large Shrinkage
- Costly
- Limited Size
What is Die Casting?
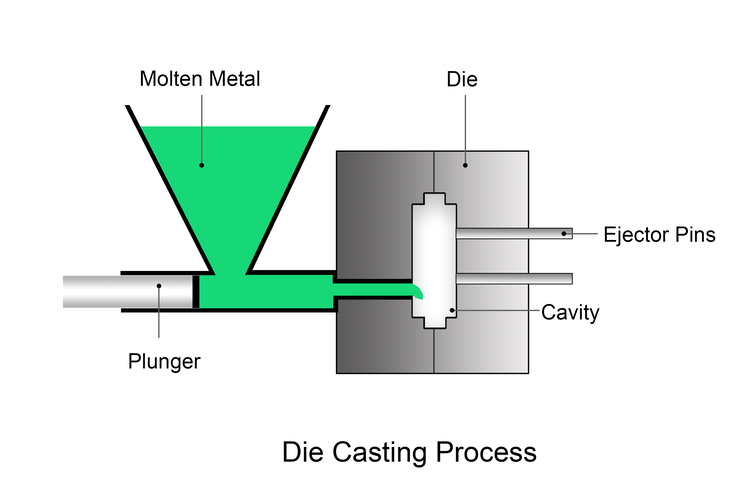
Die casting is a metal manufacturing process in which molten metal is injected into a steel mold under high pressure. It produces parts with tight tolerances, smooth surfaces, and excellent production efficiency. You may need to remove burrs and flash from die castings by trimming.
Types of Die Casting Process
Cold chamber die casting, ideal for high melting point metals, is commonly applied for materials like brass, aluminum, and zinc alloys. It separates the crucible and the injector components to avoid corrosion.
You can pour the liquid metal into the injection chamber through the pouring hole or manually scoop it.
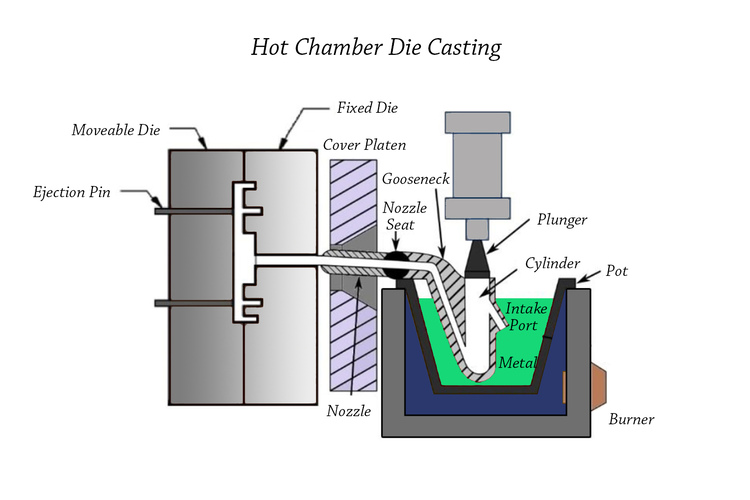
Hot chamber die casting, on the contrary, is suitable for metals with low melting points such as magnesium and zinc. The molten metal is fed into the die through a gooseneck tube with the help of a machine.
Gravity die casting turns the molten metal into the mold by gravity.
Die Casting Applications
Automotive
Die casting is applied in the automotive industry for products such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, gears, car wheels, etc.
Aerospace
Die casting could reduce the weight of the aircraft by using lightweight materials, reducing fuel consumption. typical parts are fuselages, engine piston heads, and landing gear.
Electronics
You can employ die casting to create electronic housings, heat sinks, and connectors from aluminum and zinc materials.
Die Casting Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Considerable feasibility of mass production
- Low production cost
- Can form thin-walled parts
Disadvantages
- Low material selection
- Expensive molds
- High Initial Investment

Comparison of MIM and Die Casting
Product Weight
The typical weight of metal injection molded parts is around 15 to 20g. MIM is difficult to fabricate large parts (over 50g) due to the limitations of the injection molding machine.
Die casting is able to manufacture both smaller (30g) and very large products (over 10kg).
Surface Finish
The surface roughness of metal injection molding can reach Ra 1μm. The surface of die casting is rougher about Ra 1.6-3.2 μm and you may need to trim the flash of the surface.
Material Selection
In most cases, die castings are primarily made from non-ferrous metals.
These are some common materials used in castings.
- Aluminum
- Zinc
- Brass
- Copper
- Tin
- Magnesium
- Lead
Metal injection molding, on the other hand, allows the use of a wide range of materials, including both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Here are some common MIM materials.
- Stainless Steel
- Tool Steel
- Aluminium Alloy
- Titanium Alloy
- Nickel Alloys
- Tungsten alloys
- Biocompatible Metal
Cost
Since the production cost of molds for die casting and MIM is relatively high, it is only economical to produce parts in large quantities. Casting is regularly cheaper than metal injection molding because die casting eliminates the demand for degreasing and sintering processes.
Density
Die castings are fully density, while metal injection molded parts have a density of 95% to 99%.
Shapes
MIM is able to produce small, complex parts with fine features that are difficult with die casting.
Molds
Die casting molds have a longer lifespan than MIM molds, but are also more expensive. Typically, metal injection molding tools cost between $1,400 and $2,800, while die casting tooling costs range between $1,200 and $4,200.
Production Cycle
In general, MIM green mold speed is faster than die casting. However, metal injection molded parts still need post-processing, including debinding and sintering. Therefore, the overall cycle time of die casting is shorter. Generally speaking, their production cycle, including the time to make the mold, is about 25-30 days.
Dimensional Accuracy
MIM and die casting can both achieve a dimensional accuracy of ±0.05 mm.
FAQ
1. Why is the Metal Powder Used in MIM Very Fine?
The powder particles employed in MIM are very fine, about 1–20 μm. Fine powder makes it easier to produce high-density products. The surface roughness of products made from hydroxyl iron powder can reach Ra 0.35 μm.



