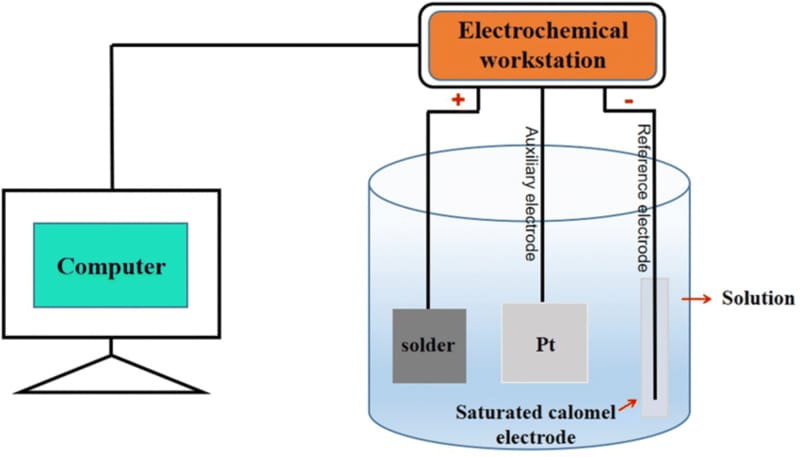
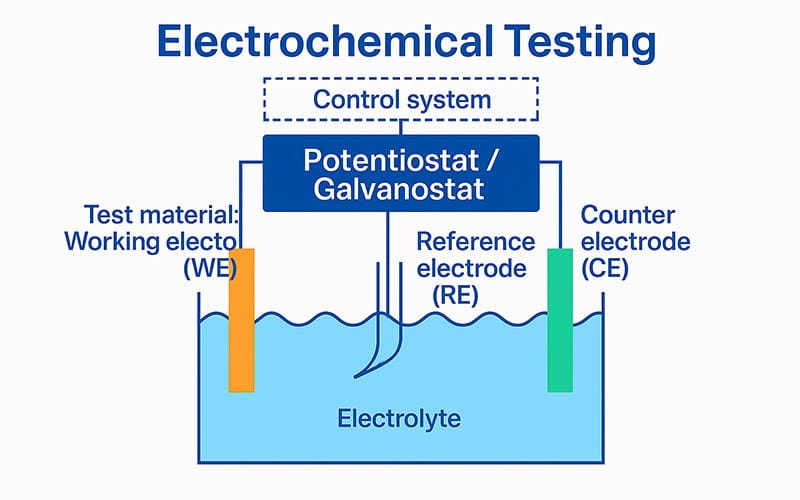
Electrochemical testing is a widely used method for evaluating the corrosion resistance of metals and alloys based on their electrochemical behavior in corrosive environments. It is typically conducted in a controlled electrochemical cell using a standard three-electrode configuration.
This technique is particularly useful for assessing components exposed to chemically aggressive or harsh environmental conditions. Under controlled laboratory settings, electrochemical testing provides a fast, precise, and reliable corrosion test method for obtaining quantitative data on metal degradation behavior.
Contents
How Electrochemical Testing Works?
During electrochemical testing, a specialized setup is used that includes an electrolyte, a reference electrode to maintain a stable voltage, a counter electrode , and the test material, which is known as the working electrode. These three electrodes are connected to a potentiostat. The reference electrode itself does not participate in the reaction, but is used only to maintain a stable reference potential.
Anodic Reaction
Anode is usually the component whose test is being done. When a potential is applied, it undergoes oxidation, and metal starts to move into the solution. The general reaction here is:
M (metal)→Mn+ + ne−
Cathodic Reaction
In a cathodic reaction, the reduction of counter electrodes or nearby areas occurs. This reduction occurs by consuming the electrons released by oxidation in anode reaction. This reaction does not involve the degradation of metal, but it promotes corrosion by accepting electrons. Common cathodic reactions, especially in neutral or basic environments where oxygen is present, are:
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
In acidic environments, the reaction may instead be:
O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
These are typical oxygen reduction reactions occuring in electrochemical corrosion testing.
Electrochemical Corrosion Testing Techniques
Potentiodynamic Polarization (PDP)
In this technique, the corrosion behavior of a metal is studied by varying the potential and studying its current output. Here, a metal sample is immersed in a corrosive solution and connected to a three-electrode system. The potential is swept typically from a cathodic to an anodic direction, and the resulting current is measured. Finally, a plot curve known as a polarization curve provides necessary information about corrosion parameters.
It tells you about:
- Corrosion potential (Ecorr): Indicates how prone the material is to corrosion.
- Corrosion current density (Icorr): Directly related to corrosion rate.
- Passivation behavior: This shows if a protective oxide layer forms and how stable it is.
- Pitting or breakdown potential: The point where localized corrosion like pitting starts.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy corrosion testing is basically a nondestructive technique. Here, you measure the resistance of the metal surface to AC over a range of different frequencies. Finally, the impedance is measured at each frequency. The data obtained is plotted on a Nyquist or Bode plot, revealing how the system behaves electrochemically.
This technique gives you information about:
- Coating performance: Detects defects, degradation, and water uptake.
- Barrier properties: High impedance = good protection.
- Charge transfer resistance: Indicates corrosion resistance at the metal/solution interface.
- The capacitance of protective films or coatings
Open Circuit Potential (OCP) Monitoring
In this technique of electrochemical testing, no external current of voltage is applied. Here, you place the sample into the electrolyte solution and measure the potential over time with the help of a reference electrode.
This technique gives information about:
- Corrosion tendency: More negative potential typically means higher corrosion risk.
- Film stability: Fluctuations may indicate the breakdown or passivation of protective layers.
Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) is a technique where the potential of the sample is swept back and forth between two set limits. Here the observation of reversible and irreversible electrochemical reactions is done. A current voltage curve is obtained whose peak indicates specific electrochemical events.
It tells about:
- Redox behavior of metals and coatings
- Formation and dissolution of passive layers
- Corrosion mechanisms such as pitting or crevice corrosion
- Reversibility of electrochemical reactions
Applications of Electrochemical Testing
Medical Device Assessment
Electrochemical testing is used to assess the corrosion in areas like crevices in medical implants and instruments.
Material Selection
It also helps engineers to identify and compare the corrosion resistance of various base materials before use in critical environments.
Surface Treatment Evaluation
This testing technique is helpful in determining how surface treatments such as passivation or coatings can alter a material’s resistance to corrosive attack.
Manufacturing Impact Analysis
Electrochemical testing also helps you monitor how different processing steps affect the material’s corrosion performance.
ASTM Electrochemical Testing Methods
ASTM G59
ASTM G59 provides a standard test method for conducting potentiodynamic polarization resistance measurements. In this method, the linear polarization of metals is measured to check out the corrosion rate. It is known for providing valuable insights into general corrosion behavior.
ASTM G85
This method provides a standard practice for modified salt spray (fog) testing. It simulates accelerated corrosion environments using variations such as cyclic exposure, acidified solutions, or SO₂ enrichment. This method is preferably used to evaluate the durability of protective coatings.
ASTM G6
To access the localized corrosion the ASTM G6 electrochemical testing method is applied. This test helps determine the susceptibility of iron-, nickel-, or cobalt-based alloys to pitting and crevice corrosion. In this method, the shape and hysteresis of polarization curves are analyzed to get the results.
ASTM G69
It is used for measuring the corrosion potentials (Ecorr) of aluminum alloys in aqueous solutions. It provides you with a ranking of alloys based on their electrochemical behavior. So, with the help of this method, galvanic interactions are predicted.
ASTM G71
This method provides you with a guide for conducting and evaluating tests between dissimilar metals in electrolytic environments. This is crucial when different metals are coupled in a corrosive setting. It helps assess the risk and extent of galvanic corrosion.
ASTM G150
It focuses on the electrochemical critical pitting temperature (CPT) testing of stainless steels and related alloys. It determines the minimum temperature at which stable pitting corrosion initiates, which is essential for qualifying stainless steel for chloride-containing environments.
Why is Electrochemical Corrosion Testing Preferred?
Speed and Real-Time Data Acquisition
Electrochemical testing is preferred by engineers to check out the corrosion resistance of material because it provides quick real-time analysis. Unlike long-term immersion tests, you can obtain them within hours.
Small Sample Size Requirement
Electrochemical testing is not only fast but requires a small amount of sample components. This makes it cost-effective and practical, especially when testing high-value components or when sample availability is limited.
High Sensitivity to Early Corrosion Stages
With the help of electrochemical corrosion testing you can detect corrosion activity long before visual signs appear. This early detection is crucial for identifying weak points in materials or coatings. It helps you to identify and prevent long-term failures, especially in critical environments.
Suitable for Coatings, Alloys, and Weld Zones
Electrochemical testing is highly adaptable and can be applied to a wide range of sample types and conditions. You can evaluate protective coatings, compare alloy corrosion resistance, or analyze the weld integrity of components. These methods provide accurate, detailed insights tailored to real-world applications.
Limitations of Electrochemical Testing
Limited to Conductive Materials
Short-Term Nature
Since in electrochemical testing the results are accelerated you may be able to get accurate results for long term corrosion behaviour.
Surface Preparation Sensitivity
One of the remarkable limitations of electrochemical testing is its sensitivity. If you do not clean the components surface properly a minute contamination can lead to false results.
Interpretation Complexity
Data analysis in electrochemical testing, such as Tafel extrapolation, polarization curves, and impedance spectra, requires expertise. Misinterpretation can lead to inaccurate conclusions about corrosion rates or mechanisms.
FAQ
1. What Factors Affect Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior?
In electrochemical corrosion testing a number of factors affect corrosion:
- Material composition
- Surface condition,
- Electrolyte chemistry
- Temperature
- Flow conditions
2. What Types of Materials Can be Tested Using Electrochemical Methods?
Electrochemical corrosion testing can be applied to conductive materials such as metals and alloys which includes:
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Coated materials



