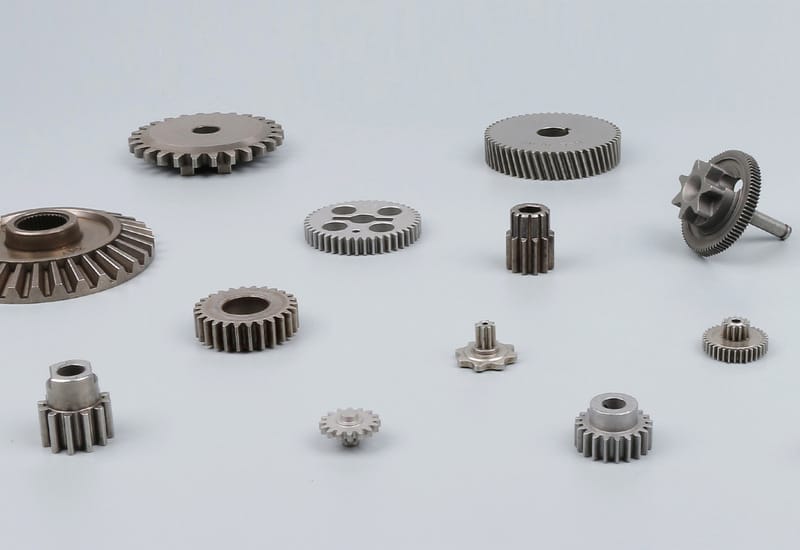
Sintered vs Machined Gears
Gears are round mechanical parts with teeth around their edges. When two or more gears mesh together, they transfer motion and torque between rotating shafts. By changing the direction, speed, or force of movement, gears play a important role in many machines and devices. Sintered