A corrosion test means exposing metal or its alloys to a controlled corrosive environment to check how well they resist rust and deterioration. Corrosion testing is usually adopted by engineers before finalizing the material to develop a specific component to predict its reliability, avoiding future failures and repairs.
These tests are also helpful in predicting the performance of coating material and how long they can protect the underneath material from damage in an aggressive environment. There are various corrosion tests that are performed according to the desired analysis, such as immersion tests, salt spray tests, electrochemical corrosion testing, crevice corrosion testing, and more.
Here are some common corrosion testing methods:
Contents
Cyclic Corrosion Testing
In cyclic corrosion testing, the material is subjected to the conditions that it may face in a real environment, such as moisture, temperature changes, and salts. But in cyclic corrosion testing, the component is not subjected to such conditions continuously. Here a component is tested in a sequence of repeated cycles where temperature, concentration of salt, and humidity keep changing, making it more realistic.
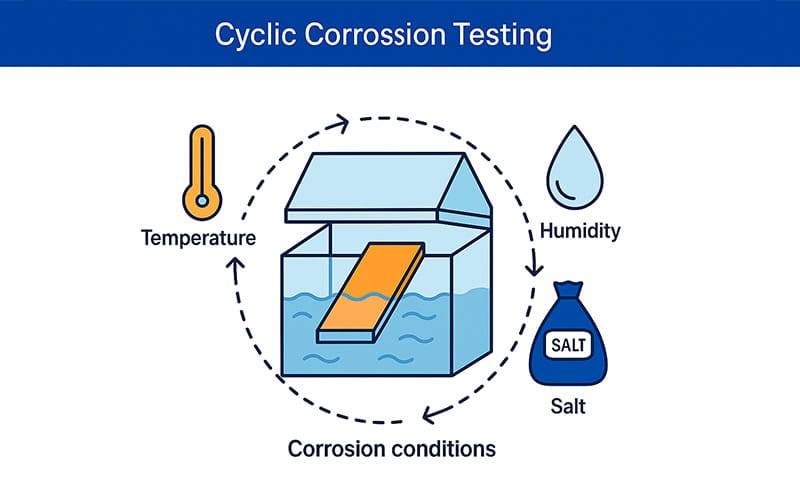
Cyclic Corrosion Testing in Automotive Industry
Cyclic corrosion testing is mainly used to predict the performance of components in the automotive industry. Here, the components are at high risk of catching corrosion due to continued exposure to moisture, salt, and changing temperature. Here is how it is done according to the DIN 55635 standard. This standard is used to predict the corrosion resistant of different coatings used on automotive parts :
- The components to be tested are placed in a test chamber at a specific angle of 65° and 75°.
- 1% NaCl solution is sprayed on the components.
- The pH is maintained between 6.5 to 7.2.
- Each full test cycle spans seven days and includes multiple stages (which are usually categorized as Cycles A, B, and C).
- The temperature of cycles keeps on changing from -15°C to high humidity and warmth at +50°C with up to 95% relative humidity.
- Usually there are 6 cycles in a standard cyclic corrosion test, and then the component is analyzed.
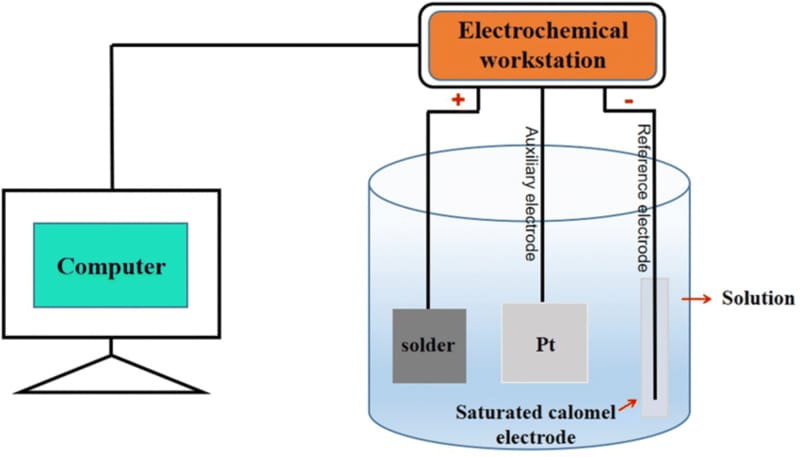
Electrochemical Corrosion Testing
Electrochemical corrosion testing method is used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of a material by analyzing its electrical properties when immersed in an electrolyte. Such tests provide accurate and precise results for the performance of material in a real-world environment. This testing method is basically divided into two types:
- Potentiodynamic Polarization: Potentiodynamic polarization is particularly useful for identifying the susceptibility of materials to localized corrosion, including pitting and crevice attack.
- Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): EIS is nondestructive and highly sensitive; that’s why it is used for long-term monitoring of corrosion resistance.
Intergranular Corrosion Test (IGC)
These tests are used to predict the intergranular corrosion in various metals and their alloys. Such corrosion usually occurs along the boundaries of grains of metal, reducing its mechanical strength and ductility. Intergranular test for corrosion are usually divided into three types:
Huey Test
The Huey test is the most commonly used method to check the IGC, especially in austenitic grade materials. In this test, the metal is exposed to a boiling 65% nitric acid solution over five consecutive 48-hour periods. After each cycle, the specimen is removed, cleaned, and weighed. The rate of weight loss indicates the degree of attack along grain boundaries.
Strauss Test
Another type of IGC testing is the Strauss test where the sample component is immersed into a boiling solution containing copper sulfate and sulfuric acid. This exposure lasts up to 72 hours and the analyzed components are then bent to check if there is any cracking or brittleness occurring. This test evaluates the material’s ductility and helps detect the presence of intergranular fissures caused by sensitization.
Streicher Test
In streicher test components are also exposed to a boiling mixture of ferric sulfate and sulfuric acid for a duration ranging from 24 to 120 hours. In this method the weight loss of the sample is measured to check the corrosion rate. This method is considered suitable for detecting corrosion in stainless steel.
Salt Spray Corrosion Test
One of the most reliable methods to check the corrosion resistance of metallic components is salt spray testing. In this test a specific salt spray test chamber is used where samples are placed at specified angles. These samples are exposed to a 5% solution of NaCl at 37°C temperature for about 24 to 72 hours. The pH of the solution is maintained between 6.5 to 7.2 for accurate results according to ISO 9227-2017 standards. After the test is complete the component is examined for any signs of corrosion, pitting or cracking.

Copper Strip Corrosion Test
This test is basically used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of petroleum based products. It helps determine whether these substances are likely to degrade copper or copper-alloy components in fuel systems and storage infrastructure. In this test a copper strip is immersed into the petroleum sample at high temperature for a specified period of time. Then the strip is examined for any signs of degradation. This test is used for:
- Quality control in fuel and lubricant production
- Monitoring sulfur levels in petroleum formulations
- Selecting compatible materials for pipelines, tanks, and engine components
- Regulatory compliance and certification testing
Immersion Test
The immersion test is considered one of the most simple and cost-effective methods to evaluate the corrosion resistance of a material. In this test the sample is also immersed into a 5% solution of salt at about 25°C to 35°C for several hours to weeks. This test falls in the category of accelerated corrosion testing, as here the corrosion is accelerated by providing harsh conditions.
The surface of the component is examined for corrosion according to various evaluating standards such as ASTM G31.This method is very helpful in designing and developing the components that are to be exposed to harsh environments, such as marine components.

Corrosion Testing Standards
Here are some corrosion test standards.
| Standard | Focus Area | Applicable Materials |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 3651-1 | Assesses resistance to intergranular corrosion | Austenitic and duplex (ferritic-austenitic) stainless steels |
| ISO 3651-2 | Evaluates intergranular corrosion susceptibility | Ferritic, austenitic, and duplex stainless steels |
| ASTM A262 | Detects susceptibility to intergranular attack through various practices | Austenitic stainless steels |
| ASTM G48 | Measures pitting and crevice corrosion resistance using ferric chloride solution | Stainless steels and corrosion-resistant alloys |
| SEP 1877 | Tests resistance to intercrystalline corrosion in high-alloy materials | High-alloy, corrosion-resistant materials |
| ISO 9227 | Conducts salt spray tests (NSS, AASS, CASS) in artificial atmospheres to assess corrosion resistance | Metallic materials with or without coatings |
| ISO 6270-2 | Determines resistance to humidity by exposing specimens to condensation-water atmospheres | Painted or coated metal surfaces |
Purpose of Corrosion Test
Evaluate Material Performance
The main purpose behind corrosion testing is to determine how metals and other materials behave when exposed to corrosive environments.
Understand Corrosion Behavior
With the help of corrosion tests, we can identify the type, rate, and mechanisms of corrosion affecting a specific material.
Material Selection
Corrosion tests provide you the essential data that helps in the selection of materials that are best for particular environments and applications.
Support Design Decisions
Corrosion tests also provide valuable insight for optimizing designs to minimize corrosion risk and extend service life.
Quality Assurance
The results from the corrosion test help you ensure that the material is suitable for the specific components and it meets the desired durability standards.
Selecting the Right Corrosion Test
How to Choose the Right Corrosion Test?
Identify the Application Environment
The first step is to know where and how the product or component will be used:
Marine Industry
The components require tests that simulate long-term saltwater exposure, such as saltwater immersion or pitting corrosion testing.
Automotive Industry
Automobile components are exposed to road salts and changing weather conditions. Therefore, they can be tested using cyclic corrosion or salt spray testing.
Aerospace Industry
In these industries, the materials are usually exposed to high altitudes and extreme temperature shifts. As a result, their reliability can be tested using cyclic testing and atmospheric exposure simulations.
Match the Test Type to the Corrosion Concern
Each test method targets specific forms of corrosion:
- Salt spray testing is effective for assessing general resistance to salty, humid environments.
- In cyclic corrosion testing, you can simulate real-world conditions through alternating phases of humidity, drying, and temperature changes.
- Immersion testing is considered ideal for continuous exposure to liquids or chemicals, and it is often used in marine or industrial contexts.
Applications of Corrosion Test Methods
Corrosion tests are extensively used in industries such as
Automotive Industry
In the aerospace industry, the components’ mechanical strength and integrity are assured by performing corrosion tests. These tests are implemented on the body parts of a vehicle and suspension elements to ensure their durability and longevity.
Aerospace Industry
The components of aircraft usually remain in contact with air moisture and salt; that is why they are at high risk of catching corrosion. As a result, in the aerospace industry, before developing a component, the material is subjected to corrosion tests to check its reliability.
Electronic Components
The corrosion resistance of materials to develop different electrical devices such as capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits is evaluated with the help of corrosion tests. These tests ensure that the components will not cause any failure while working.
Medical Devices
Corrosion tests, such as immersion tests and salt spray tests, give precise and accurate results for the corrosion resistance of a material; that is why they are used for medical instruments.



