Pressing is an effective way to form powder particles into components. However, the compacted parts often lack strength and are easily broken.
Sintering process resolves this issue, giving the parts the necessary strength and density. Sintering takes place in a sintering furnace.
According to the quantity and characteristics of your products, we need to choose different sintering furnaces
Contents
Sintering in Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is the process of heating compacted powders to give them strength and structural integrity, just below their melting point. It mainly includes the following three stages.
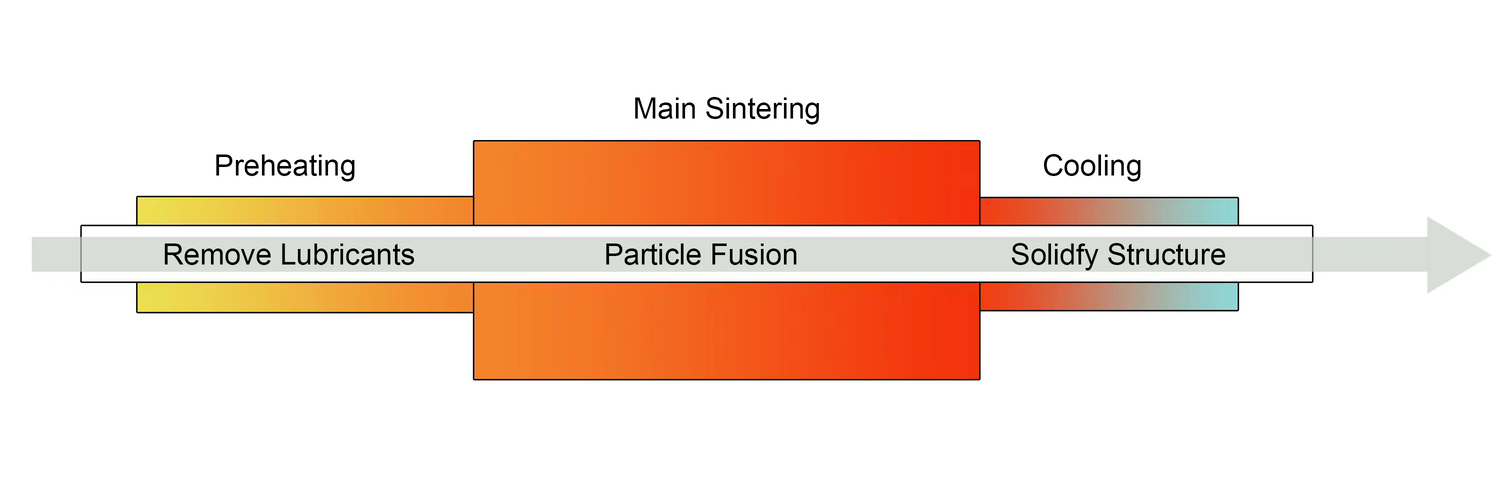
1. Pre sintering in powder metallurgy
The primary purpose of pre-sintering is to remove binders. In this process, you heat the green compact to 600-900°C for about 30 minutes.
2. High Temperature Sintering
During high-temperature sintering process, atoms in the metal powder diffuse across particle boundaries and fuse to form a solid piece.
During this process, the atoms in the metal powder diffuse beyond the particle boundaries and fuse to form a solid.
3. Cooling
The sintered particles need to be fully solidified, and you should remove the thermal stress of the product. So the cooling process is necessary. Usually, the cooling time is about 2 hours.
Types of Sintering
- Solid state sintering occurs at the melting point of all metallic materials
- Liquid phase sintering is the process of introducing liquid elements to accelerate the densification between powder particles, thereby promoting sintering.
- Spark plasma sintering (SPS) applies high-density pulsed electric current to turn powder into a solid. The process occurs in a controlled environment.
Types of Sintering Machines
Conveyor Belt Furnace
Conveyor belt furnace is a continuous sintering machine
The conveyor belt furnace consists of 3 chambers:
- Presintering chamber
- Primary sintering chamber
- Cooling chamber
Due to the creep concerns of the conveyor belt at high temperatures, the operating temperature of the conveyor belt furnace is generally below 1150°C. Therefore, conveyor belt furnaces are generally suitable for iron-based and copper-based products.
Conveyor belts are mostly made of 310 stainless steel. But 314 stainless steel and Inconel® 601 have better high temperature resistance. The disadvantage of this sintering machine is that the mesh belt is easily oxidized and carbonized, thereby reducing its service life.
Besides, the conveyor belt speed is about 50 to 250 mm/min. And the width of the conveyor belt is about 500mm.
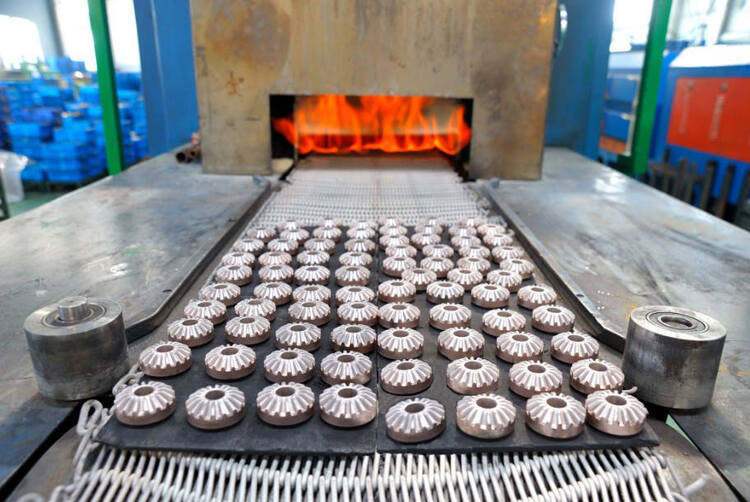

Pusher Furnace
The pusher sintering furnace is also a continuous furnace, known for its fast production rate.
The push rod pushes the product into the furnace without a conveyor belt. In addition, pusher furnace is automatic.
The sintering temperature of the push rod furnace is often above 1200°C, and the highest can reach 2200°C.
This is because there are no moving parts in the heat treatment area of pusher furnace, so it has a higher operating temperature.
The operation of a pusher furnace generally includes:
- Loading: First, you load the green components onto the pusher plate or pusher outside the furnace.
- Pushing: The pusher furnace pushes the components through the preheating zone and main sintering zone of the furnace at a controlled speed.
- Unloading: The sintered product is unloaded by the pusher plate or pusher for secondary processing.

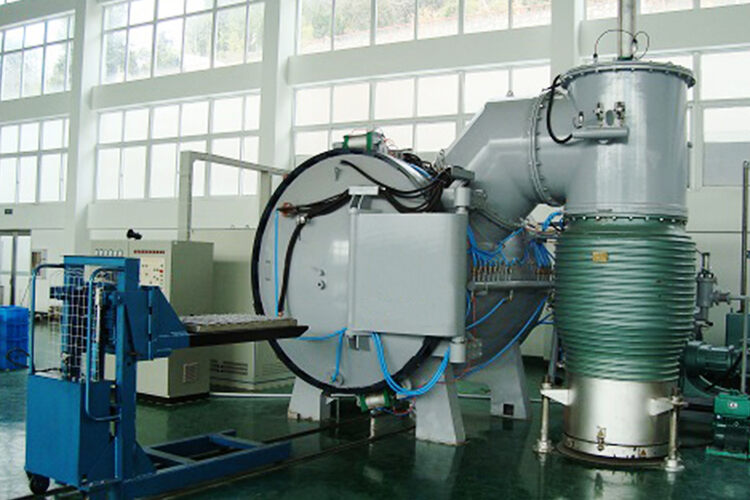
Vacuum Sintering Furnace
As we all know, continuous furnaces are suitable for large-batch production. On the contrary, batch furnaces, like vacuum sinteirng furnace are suitable for small order quantities.
Or when the sintering temperature and time are different for each product, a batch furnace is more cost-effective.
Vacuum furnaces can save the cost of protective atmosphere.
Vacuum sintering furnaces can achieve higher temperatures than conveyor belt furnaces, reaching 2500°C or even higher.
And with no gas inside the product to cause pore shrinkage, it becomes easier to densify.
Therefore, for those sintering times that are long or protective atmosphere is expensive, vacuum furnaces are more economical. Especially for high-temperature metals such as stainless steel, tungsten carbide, molybdenum, etc.

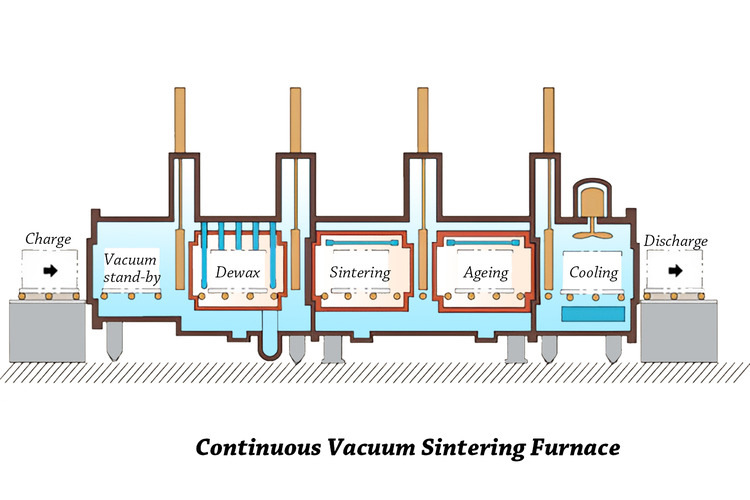
Continuous Vacuum Furnace
Since the batch vacuum furnace takes a long time to heat up and down and evacuate, and has a small production capacity, the continuous vacuum furnace came into being.
This sintering furnace includes three chambers: degreasing chamber, sintering chamber, and cooling chamber. Different chambers are separated by partitions.
Walking Beam Furnace
Walking beam sintering furnace is also a continuous furnace, with a maximum sintering temperature of 1800℃. These furnaces adopt a unique reciprocating motion to shuttle the product through the sintering machine. This motion mechanism allows the product to be evenly exposed to the required temperature zone.
Generally, walking beams are utilized only in the sintering zone, the dewax zone uses a pusher mechanism, and the cooling zone uses a conveyor system. These three zones form a closed system, which will greatly reduce the consumption of protective gas.
Sintering Furnace Prices
The following is a comparison of conveyor belt furnaces and vacuum sintering furnaces, including prices.
| Type | Conveyor Belt Furnace | Vacuum Sintering Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 75KW | 80KW |
| Max Temperature | 1150°C | 1600°C |
| Temperature Control Accuracy | ±1°C | ±1°C |
| Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C | ±5°C |
| Chamber Size (L*W*H) | 6000*300*60mm | 450*300*300mm |
| Temperature Rising Time | ≤3H | / |
| Output | 100KG/H | 200kg/per furnace |
| Ultimate Vacuum | / | 5×10⁻³ Pa |
| Cost | $25,000 | $22,000 |
Recommended Sintering Furnace Manufacturers
Abbott Furnace Company
Abbott Furnace Company is a professional industrial furnace manufacturer located in the United States.
Their equipment includes sintering machines, annealing furnaces, tempering furnaces, heat treatment machines, etc.
Sentro Tech
Sentro Tech, founded in 1992 and headquartered in Ohio, is a professional high-temperature furnace manufacturer.
They have a complete line of high-temperature processing technology products. In addition, they also provide customers with high-temperature furnace replacement parts, including heating elements, fiberboards.
Gasbarre
Gasbarre is headquartered in Pennsylvania, USA, and specializes in powder metallurgy equipment.
Their equipment includes powder forming and shaping presses, vacuum sintering furnaces, conveyor belt furnaces, etc. Besides, they specialize in the design and production of custom sintering furnaces.
Ningbo East Heating Equipment
Ningbo East Heating Equipment is a company that specializes in industrial furnaces.
They are committed to the research and development and production of advanced mesh belt sintering furnaces, push plate sintering furnaces, steam treatment furnaces and iron powder fine reduction furnaces.
FAQ
1. Are Heat Treatment Furnaces the Same as Sintering Furnaces?
No.
Heat treatment and sintering are different processes. The temperature of the heat treatment furnace is usually 700-800 °C, and the temperature of the sintering furnace is often over 1000 °C.
2. How Long Is the Conveyor Belt Furnace?
The conveyor belt furnace includes preheating area, sintering area and cooling area. The conventional conveyor belt furnace is about 20-30 meters.
3. What Are the Outputs of Pusher Sintering Furnace and Conveyor Belt Sintering Furnace?
The daily output of the conveyor furnace is about 2-3 tons, and the push rod furnace is higher, about 5 tons.
4. What is the General Sintering Temperature of Powder Metallurgy Parts?
- Copper sintering temperature: 800°C
- Iron sintering temperature: 1120°C
- Stainless steel sintering temperature: 1250°C
- Iron-copper alloy sintering temperature: 900°C
5. What are the Sintering Atmospheres?
The sintering atmosphere will affect the mechanical properties, appearance and corrosion resistance of your products. Therefore, the sintering atmosphere is very important. The main functions are as follows:
- Prevent the outside air from entering the sintering furnace and causing product oxidation
- It helps to reduce the binders in the parts
- It reduces the oxide layer on the surface of the compacted powder
- Control the carbon content of the product
The sintering atmospheres we commonly use include:
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Argon
- Vacuum



